Microscopic and Spectroscopic Characteristics of CVD Synthetic Blue Diamond
-
摘要:
天然蓝色钻石产量稀少且价格昂贵,主要流通于高端拍卖市场。随着市场需求增长,合成及改色处理的蓝色钻石逐渐进入人们的视野。目前,常见的高温高压法(HPHT)合成的掺硼蓝色钻石常因生长分区形成了十字形的颜色分布特征,人工辐照改色蓝色Ⅰa型钻石的蓝绿色调受N3和GR1两个色心的强弱控制,Ⅱa型钻石辐照后颜色主要受GR1色心控制,同时GR2-8色心辅助致色,因无法人为定量控制色心的强弱,颜色具有不稳定性。化学气相沉积法(CVD)合成钻石在硼元素掺杂致色的浓度、均匀程度及一致性调控方面更具优势,但由于其生长难度较大,目前少见CVD法生长合成蓝色钻石的报道。本研究通过放大检查、紫外-可见吸收光谱、红外光谱、拉曼光谱以及光致发光光谱对一颗CVD合成的蓝色钻石进行一系列光学无损表征测试,并与天然蓝色钻石和辐照改色蓝色钻石对比。结果发现, CVD合成的含硼蓝色钻石与天然蓝色钻石颜色相近,颜色分布较为均匀,内部干净,少数有羽状纹和暗色物质;紫外-可见光谱吸收特征与天然蓝色钻石相似,但区别于辐照处理蓝色钻石的GR1色心吸收带(741 nm);红外光谱表明样品为Ⅱb型钻石,1 290 cm-1和2 458 cm-1处与硼相关吸收峰与天然蓝钻的2 455 cm-1和2 802 cm-1处吸收峰以及辐照改色蓝色钻石中由H1a心引起的1 450 cm-1处吸收峰存在差异,且三声子区(>3 000 cm-1)的波动表明硼含量高;CVD合成蓝色钻石的拉曼光谱在1 332 cm-1处的金刚石本征峰因硼掺杂呈现不对称;光致发光光谱测试结果表明,样品存在[NV]0缺陷(575 nm)、[NV]-缺陷(637 nm)以及[SiV]-缺陷(737 nm)。
Abstract:Natural blue diamonds are produced in very small quantities and command extremely high prices, mostly appearing in the auction market. With the increasing demand for blue diamonds, some synthetic or colour modified blue diamonds came into people's view. At present, common boron-doped blue diamond synthesized by high temperature and high pressure (HPHT) method tend to have a cross-shaped colour distribution characteristic of growth zoning. Irradiated type Ia blue diamonds display blue-green hues controlled by the relative intensities of N3 and GR1 colour centers. Irradiated type Ⅱa diamonds primarily show GR1-dominated colouration with GR2-8 colour centers as auxiliary contributors, so we can't control the intensity of the colour center in an artificial and quantitative way, which results in the colour being unstable. Diamond synthesized by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) has distinct advantages in controlling doped boron element concentration and maintaining uniformity and consistency. However, due to the difficulty of its growth, there are few reports of blue diamonds synthesized by CVD. In this study, a blue diamond synthesized by CVD was performed a series of optical non-destructive characterization tests by magnification examination, ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer, infrared spectrometer, Raman spectrometer, and photoluminescence spectrometer. Comparing with irradiation modified and HPHT blue diamonds, this boron doped blue diamond synthesized by CVD was similar to natural blue diamonds in colour, with a more uniform colour distribution, clean inclusion, and a few feather and dark substances. UV-Vis spectra showed that the absorption features of the CVD synthetic blue diamonds are similar to the natural blue diamonds but distinct from the GR1 center absorption band (741nm) in irradiation-treated diamonds. The infrared spectra revealed the sample to be a type Ⅱ b diamond. The boron-related absorption peaks at 1 290 cm-1 and 2 458 cm-1 differed from the 2 455 cm-1 and 2 802 cm-1 peaks observed in natural blue diamonds, as well as the 1 450 cm-1 peak associated with the H1a defect center in radiation-treated blue diamonds. Additionally, fluctuations in the three-phonon region (>3 000 cm-1 ) suggested a high boron content. Raman spectra exhibited 1 332 cm-1 diamond intrinsic asymmetry peak resulting from boron doping. Photoluminescence spectroscopy tests revealed the presence of [NV]0 defects (575 nm), [NV]-defects (637 nm), and [SiV]-defects (737 nm).
-
Keywords:
- blue diamond /
- chemical vapor deposition method /
- synthesis /
- irradiation /
- identification
-
在众多蓝色宝石中,蓝色钻石不仅拥有如大海般清澈美丽的颜色,还具备无可比拟的火彩与亮度。蓝色钻石在自然界十分稀有,因此被视为珠宝届最昂贵且独特的存在。近年来,随着人们对个性化需求的日益增强,象征自由与浪漫、色彩绚烂的蓝钻受到广泛追捧,并屡次刷新拍卖场中的最高成交额。例如,在2022年4月27日,一颗名为“De Beers戴比尔斯浩宇之蓝”的15.1 ct长方形阶梯式切割艳彩蓝钻,在香港苏富比拍卖会上以5 750万美元成交,创下了钻石拍卖新的里程碑[1]。此外,Hope Diamond[2]、Blue Heart Diamond(也称为Unzue或Eugsamnie blue)[3]和Idol’s Eye Diamond[4]等历史上重要的蓝色钻石,也为其增添了魅力和神秘感。
伴随着全球合成钻石产业的快速发展,珠宝市场上逐渐出现通过高温高压(HPHT)法和辐照优化处理的合成蓝色钻石。硼掺杂是合成蓝色钻石的途径之一,其中采用固态含硼碳源在高温高压条件下溶解于金属触媒,碳源由高温端扩散至低温端,并在钻石晶种上生长形成蓝色钻石晶体[5]。相较于其他方法,高温高压法技术具有速度快、成本低等优点,但其合成蓝色钻石的纯净度相对较差且颜色分布不均匀。相关研究[6-8]表明,硼元素在八面体生长区的含量最高,四面体生长区最低,同时存在无色和有色交替的区域。相比之下,天然钻石可能会显示出平面色带或褶皱效果,而不会出现与内部生长区相关的图案[9]。人工辐照改色技术是目前市场上具有蓝色调钻石的主要处理技术之一。这类因辐射处理而呈现蓝色的钻石可分为Ia型和Ⅱa型,其辐照原理是通过电子辐照引入缺陷中心GR1色心,其中,GR1色心的零声子峰吸收峰为740.9 nm,并在430~412 nm范围内形成一个宽吸收带[10]。Ia型钻石同时具备N3色心及GR1色心,N3色心吸收短波可见光,GR1色心吸收长波可见光,这两个色心的相对强弱关系决定了钻石呈蓝色还是绿色[11-12]。Ⅱa型钻石辐照后主要受GR1色心的影响,GR2-8色心辅助致色,GR1色心常伴随GR2-8的吸收峰。GR1色心本身使钻石产生蓝色,当GR2-8色心变得更为显著时,它们在光谱的蓝绿区域产生额外的吸收,钻石颜色为偏绿的蓝色[8]。人工辐照改色钻石的颜色分布位置和形状会受辐照方向的影响,有时靠近轰击源一侧颜色会出现加深现象[13];同时人为精准定量控制色心浓度较为困难。辐照处理蓝色钻石具有GR1辐照色心(741 nm),不可见硼的典型吸收峰(2 800 cm-1),与天然蓝色钻石具有明显区别[14]。
化学气相沉积法(CVD)是目前人工合成高品质钻石的核心技术之一,其工艺原理主要是通过相对较低的温度(800 ~ 1 000 ℃)或者真空环境下,气态或液态碳源(如甲烷、乙醇等)在氢气气氛裂解生成活性碳原子,并在单晶钻石种晶片基底上实现外延逐层生长[7, 15]。该技术制备的合成钻石晶体纯度高、结晶度好、沉积速度快及表面形貌均匀等特性。相较于高温高压法(HPHT),CVD法虽然成本高,但在晶格的均匀性控制方面更具优势。目前,国内外关于CVD合成掺硼钻石的研究主要集中于半导体性能应用,受限于气态和液态的硼源(如乙硼烷)的毒性,仅有少数机构掌握CVD合成掺硼钻石的生长技术,从而导致这类合成蓝色钻石的宝石学特征研究资料较少。
尽管上述不同方式生产蓝色钻石的研究成果及资料丰富,但实验室CVD合成掺硼钻石的特征研究尚未充分开展,且不同合成方法的蓝色钻石在显微特征、谱学特征上具有差异性。鉴于此,本研究选取方形CVD合成蓝色钻石样品,通过放大检查、紫外-可见吸收光谱(UV-Vis)、拉曼光谱、红外光谱(FTIR)、光致发光光谱(Photoluminescence)等测试方法对其进行系统表征,并与天然Ⅱb型蓝色钻石及辐照改色蓝色钻石的致色成因进行对比,为以后实验室中此类产品的鉴定提供一些参考依据。
1. 样品及测试方法
1.1 样品情况
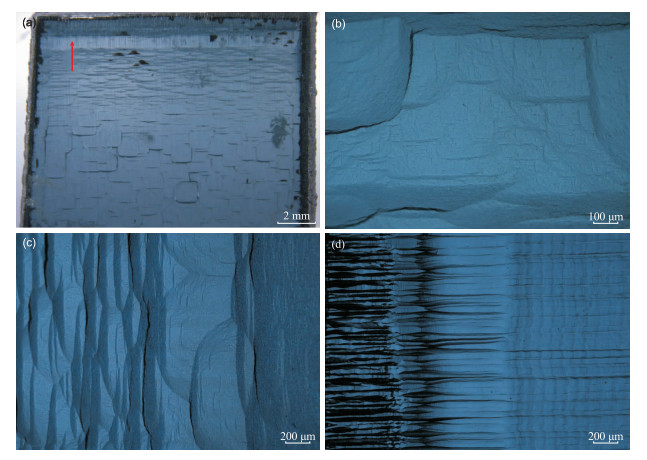
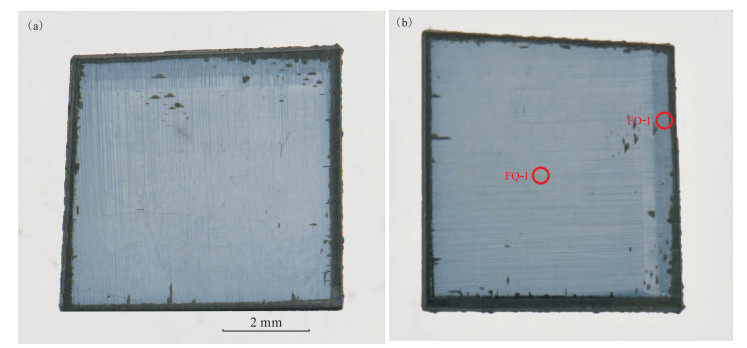
本研究中测试样品为一颗近方形的蓝色合成钻石(图 1),由6C Technology Limited公司通过微波等离子体化学气相沉积法以甲烷为碳源引入固态硼源生长而成,其尺寸为12 mm×13 mm×3 mm,总体蓝色分布均匀,有轻微色调深浅的区分,四周边缘有约1 mm宽的黑色石墨化区域,具有典型的CVD生长特征。
1.2 测试方法
放大检查及显微拍照使用Leica M205A高分辨显微体式照相机对CVD合成蓝色钻石样品的内、外部特征进行图像采集;紫外-可见吸收光谱测试采用JASCO Msv-5200型显微紫外-可见-近红外光谱仪,测试方法为透射法,取样区域直径为100 μm,测试条件:光谱采集范围300~850 nm,数据间隔0.5 nm,扫描速度1 000 nm/min;红外光谱测试采用Bruker Vertex 80型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪,测试条件:测试范围1 000~4 500 cm-1,分辨率4 cm-1,扫描次数32次;拉曼光谱与光致发光光谱测试均使用JASCO NRS7500型拉曼光谱仪,测试条件:激发光源532 nm,拉曼光谱的测试范围400~1 500 cm-1,PL光谱的测试范围550~800 nm,数据间隔0.1 cm-1,采集次数均为2次。以上测试均在中国地质大学(武汉)珠宝学院完成。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 显微特征
CVD合成蓝色钻石样品呈现均匀的颜色分布特征,以浅蓝色为主,在靠近晶片边缘位置,颜色较深,且其间还出现了宽约1 mm的浅色带(见图 2a箭头所示)。放大观察显示,合成蓝色钻石样品整体呈现典型的层状生长结构:其截面表现为周期性阶梯状堆叠结构,表面可见树枝状生长纹,且观察到明显的生长台阶(图 2b和图 2c);内部纯净度和透明度较高,具少量暗色包裹体,其边缘棱处暗色区域呈条带状分布(图 2d)。以上显微特征均为CVD合成钻石的典型特征。
2.2 紫外-可见光谱分析
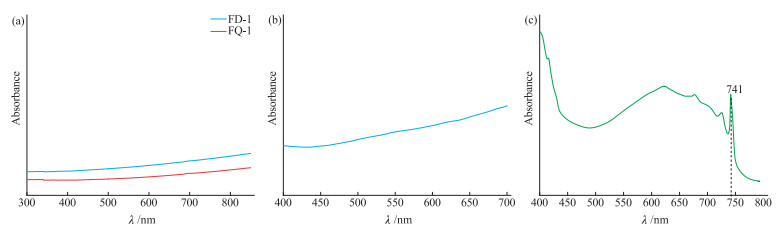
在合成蓝色钻石样品中选取深色测试点位FD-1和浅色测试点位FQ-1(图 1b)进行紫外-可见光谱测试。结果(图 3)显示,深色点位FD-1和浅色点位FQ-1的紫外-可见光谱基本一致,从红光到蓝光的吸收逐渐减弱,允许大量来自绿色、黄绿色和橙红色区域的光线透过,从而产生蓝色色调。其中,深色点位FD-1处的吸收峰更强,硼元素含量更高,故而其颜色饱和度更高[16]。
与天然蓝色钻石的紫外-可见吸收光谱对比(图 3a和图 3b)表明,合成蓝色钻石样品中2个测试点位的谱图与天然蓝色钻石的十分接近,均表现出较为平缓的可见光吸收,据此也可以判定二者颜色的一致性[10]。辐照处理蓝色钻石的紫外-可见吸收光谱(图 3c)呈现典型的741 nm处GR1色心,与其相关的宽吸收带从约550 nm延伸至750 nm,对大部分黄光到红光产生吸收,在400~500 nm范围蓝光区和部分绿区内形成透过窗口,从而使钻石呈现微绿蓝色,与本文合成蓝色钻石样品以及天然蓝色钻石的紫外-可见光谱差异较明显[17]。
2.3 红外光谱分析
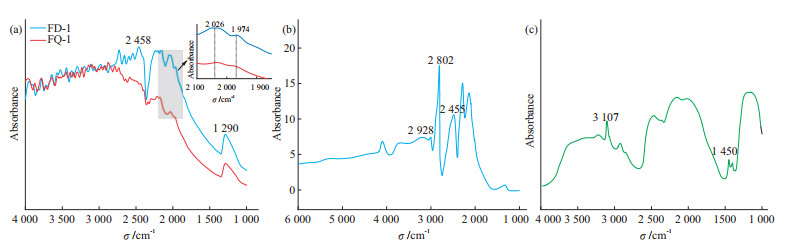
合成蓝色钻石样品中深色测试点位FD-1和浅色测试点位FQ-1的红外光谱结果(图 4)显示,该样品为Ⅱb型钻石,主要位于1 974 cm-1和2 026 cm-1处的钻石本征吸收峰(图 4a);在1 290 cm-1和2 458 cm-1处的特征吸收峰,与掺硼蓝色钻石中的硼元素相关联,结合紫外-可见光谱结果以及张圣亚[19]研究,笔者推测,点位FD-1中硼含量更高。在超过3 000 cm-1的高波数的三声子区域,CVD掺硼合成钻石的谱线呈波动状态,这与高浓度的硼有关[20]。
本研究样品的红外光谱与天然蓝色钻石有一定的差别,天然蓝色钻石的红外光谱(图 4b)在2 455、2 802 cm-1和2 928 cm-1处的吸收峰是由于硼原子取代金刚石晶格中的碳原子时,硼原子比碳少一个价电子,会在带隙中引入一个受主能级,改变了晶格振动模式[17],结果显示样品与天然蓝色钻石均为硼元素致色。而辐照蓝色钻石的红外光谱(图 4c)常见3 107 cm-1处的吸收峰,由C-H的振动吸收峰所致。同时还可见H1a色心(位于1 450 cm-1处),说明其经过人工辐照[11, 21]。这三类蓝色钻石的红外光谱区别较大,鉴别特征明显。
2.4 拉曼光谱与光致发光光谱分析
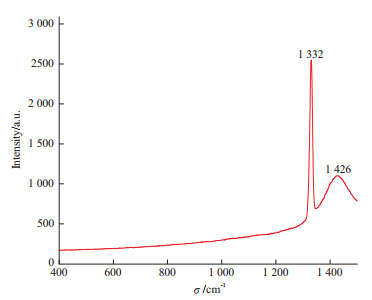
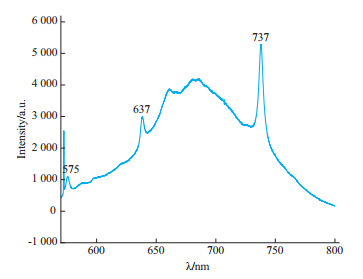
拉曼光谱测试结果(图 5)显示,在532 nm的激发光源下,CVD合成蓝色钻石样品可见1 332 cm-1处的钻石拉曼本征峰,对称性略差,其半宽高(11 cm-1)高于未掺杂的CVD合成钻石(3 cm-1)[22];具有较好的结晶度,在1 580 cm-1未见石墨的特征峰[23-24]。钻石的拉曼本征峰的不对称以及较宽的半宽高与掺杂硼元素导致的Fano效应有关[25-27];位于1 426 cm-1处的特征峰与光致发光光谱中的575 nm相对应,为电中性的氮空位缺陷的典型特征。
光致发光光谱测试结果(图 6)表明,在532 nm的激发光源下,该掺硼蓝色合成钻石样品中可激发较强的575 nm的[NV]0和637 nm的[NV]-荧光,并且在737 nm处还发现了Si杂质和空穴结合形成的[SiV]-特征峰[28-29],氮空位(NV)中心和硅空位(SiV)中心是CVD法生长钻石过程所引入的典型缺陷。
3. 结论
(1) CVD合成蓝色钻石样品表现了较均匀的颜色分布与较高的纯净度,可见阶梯状生长纹理及少量暗色包裹体,这是CVD合成钻石的典型特征之一。与其他方法合成蓝色钻石相比,CVD合成蓝色钻石整体的纯净度、透明度较高,且尺寸较大。
(2) CVD合成蓝色钻石样品的紫外-可见光谱显示其由硼元素致色,表现为平缓的可见光吸收带,从红光到蓝光的吸收逐渐减弱,大量来自绿色、黄绿色和橙红色区域的光线透过,产生蓝色色调。CVD合成蓝色钻石与天然蓝色钻石颜色表征极为相似,均由硼元素掺杂致色。与辐照处理蓝色钻石区别较大,主要体现在741 nm处GR1色心引起的宽吸收带上。此外,CVD合成蓝色钻石中颜色饱和度与硼掺杂浓度呈正相关,进一步验证了硼元素的致色作用。
(3) CVD合成蓝色钻石样品的红外光谱显示其为Ⅱb型钻石,位于1 290 cm-1和2 458 cm-1处的吸收峰与硼元素相关,大于3 000 cm-1的三声子区域出现强烈波动,与较高的硼含量有关。天然蓝色钻石虽同为硼致色,但其特征峰主要位于2 455 cm-1和2 802 cm-1处,与本文样品存在差异;辐照蓝色钻石则通过3 107 cm-1处的C-H吸收峰及1 450 cm-1处的H1a色心与前两者区分。红外光谱的差异性为三类蓝色钻石的鉴别提供了关键依据。
(4) CVD合成蓝色钻石在样品1 332 cm-1处的拉曼峰的不对称以及较宽的半宽高与硼掺杂导致Fano效应有关;光致发光光谱测试其表面存在氮空位(NV)中心和硅空位(SiV)中心,为CVD生长过程中引入的典型杂质缺陷。天然蓝色钻石及辐照改色蓝色钻石不可见此类特征峰。
-
-
[1] De Beers. 戴比尔斯浩宇之蓝香港苏富比创下钻石拍卖一个新的里程碑[J]. 中国拍卖, 2022(6): 44-45. De Beers. De Beers Aquamarine Sotheby's Hong Kong sets a new milestone in diamond auctions[J]. Chinese Auction, 2022(6): 44-45. (in Chinese)
[2] Patch S S. Blue mystery: The story of the Hope Diamond[M]. Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1976.
[3] Gaillou E, Post J E, Rost D, et al. Boron in natural type Ⅱb blue diamonds: Chemical and spectroscopic measurements[J]. American Mineralogist, 2012, 97(1): 1-18. doi: 10.2138/am.2012.3925
[4] Leighton R. The duke of brun swicks's diamonds[J]. Good Words, 1864(5): 7-7.
[5] 王志文, 马红安, 陈良超, 等. 硼协同掺杂金刚石单晶的高温高压合成[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2022, 51(5): 830-840. Wang Z W, Ma H A, Chen L C, et al. HPHT synthesis of boron co-doped single crystal diamond[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2022, 51(5): 830-840. (in Chinese)
[6] 白皓. 金刚石硼杂质色心的制备及其光致发光研究[D]. 太原: 太原科技大学, 2023. Bai H. Preparation and photoluminescence of boron impurity center in diamond[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, 2023. (in Chinese)
[7] Chepurov A I, Yelisseyev A P, Zhimulev E I, et al. High-pressure, high-temperature processing of low-nitrogen boron-doped diamond[J]. Inorgaic Materials, 2008(44): 377-381.
[8] 付守庆, 张彩慧, 安群彦. 天然、合成与处理蓝色钻石的致色机理研究[J]. 山东工业技术, 2018(19): 11-12, 3. Fu S Q, Zhang C H, An Q Y. Study on the chromogenic mechanism of natural, synthetic and treated blue diamonds[J]. Shandong Industrial Technology, 2018, (19): 11-12, 3. (in Chinese)
[9] Shigley J E, Fritsch E, Reinitz I, et al. A chart for the separation of natural and synthetic diamonds[J]. Gems & Gemology, 1995, 31(4): 256-264.
[10] 王雅祺. 蓝色钻石的宝石学特征及鉴定[J]. 超硬材料工程, 2020, 32(4): 47-51. Wang Y Q. Gemmological characteristics and identification of blue diamonds[J]. Superhard Material Engineering, 2020, 32(4): 47-51. (in Chinese)
[11] 徐速, 夏玉梅, 曲蔚. 辐照改色处理蓝色Ⅰa型钻石的光谱学特征[J]. 宝石和宝石学杂志(中英文), 2023, 25(2): 1-5. Xu S, Xia Y M, Qu W. Spectroscopic characteristic of irradiated and annealed blue type Ⅰa diamond[J]. Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2023, 25(2): 1-5. (in Chinese)
[12] 张彩慧, 陈美华. 电子辐照产生蓝色钻石的工艺条件探索[J]. 宝石和宝石学杂志(中英文), 2016, 18(4): 10-15. Zhang C H, Chen M H. Research on treatment method of electron irradiated blue diamond[J]. Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2016, 18(4): 10-15. (in Chinese)
[13] 张蓓莉. 系统宝石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006: 144. Zhang B L. Systematic gemmology[M]. Beijing: GeologyPress, 2006: 144. (in Chinese)
[14] 李倩, 李文宣. 合成及改色钻石的鉴定特征[J]. 宝石和宝石学杂志(中英文), 2014, 16(6): 21-27. Li Q, Li W X. Identification characteristics of synthetic and colour-altered diamonds[J]. Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2014, 16(6): 21-27. (in Chinese)
[15] 何珊珊, 谭红琳, 祖恩东. 天然钻石和合成钻石的光谱学特征研究[J]. 光散射学报, 2022, 34(2): 179-186. He S S, Tan H L, Zu E D. Comparative study on the spectral characteristics of natural diamond and synthetic diamond[J]. The Journal of Light Scattering, 2022, 34(2): 179-186. (in Chinese)
[16] Green B L, Collins A T, Breeding C M. Diamond spectroscopy, defect centers, color, and treatments[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2022, 88(1): 637-688.
[17] King J M, Moses T M, Shigley J E, et al. Characterizing natural-color type Ⅱb blue diamonds[J]. Gems & Gemology, 1998, 34(4): 246-268.
[18] Eaton-Magaña S, Breeding C M, Shigley J E. Natural-colorblue, gray, andviolet diamonds: allureof the deep[J]. Gems & Gemology, 2018, 54(2).
[19] 张圣亚. 蓝色钻石内部缺陷分析与形成机制研究[D]. 济宁: 曲阜师范大学, 2021: 44. Zhang S Y. Study on the analysis of internal defects and formation mechanism of blue diamonds[D]. Jining: Qufu Normal University, 2021: 44. (in Chinese)
[20] Fangqing Z, Erqing X, Bin Y, et al. Synthesis and infrared absorption characteristics of boron-doped semiconducting diamond thin films[J]. Materials Letters, 1994, 19(3-4): 115-118.
[21] 朱红伟, 李婷, 燕菲, 等. 一粒经辐照处理的蓝色钻石的鉴定特征[J]. 超硬材料工程, 2017, 29(6): 62-64. Zhu H W, Li T, Yan F, et al. Identification characteristics of the irradiated blue diamond[J]. Superhard Material Engineering, 2017, 29(6): 62-64. (in Chinese)
[22] 罗伯诚, 罗湘捷, 丁立业. 高含硼金刚石的一阶Raman谱特性分析[J]. 原子与分子物理学报, 2000, 17(1): 67-70. Luo B C, Luo X J, Ding L Y. The analyses of properties of the first-order Raman spectrum of the diamond with a high component of boron[J]. Journal of Atomic and Molecular Physics, 2000, 17(1): 67-70. (in Chinese)
[23] 梁榕, 兰延, 陆太进, 等. Renishaw-inVia激光共焦显微拉曼光谱仪在CVD合成钻石鉴定中的应用[C]//珠宝与科技——中国珠宝首饰学术交流会论文集(2015). 北京: 中国宝石, 2015. Liang R, Lan Y, Lu T J, et al. The application of renishaw. in Via laser confocal micro raman spectrometer on the identification of CVD synthetic diamond[C]//Jewelry and Technology-Proceedings of China Jewelry Academic Exchange Conference(2015). Beijing: China Gems, 2015. (in Chinese)
[24] Prawer S, Nemanich R J. Raman spectroscopy of diamond and doped diamond[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2004, 362(1 824): 2 537-2 565.
[25] Li H, Zhang T, Li L, et al. Investigation on crystalline structure, boron distribution, and residual stresses in freestanding boron-doped CVD diamond films[J]. Journal of crystal growth, 2010, 312(12-13): 1 986-1 991.
[26] Crisci A, Mermoux M, Saubat-Marcus B. Deep ultra-violet Raman imaging of CVD boron-doped and non-doped diamond films[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2008, 17(7-10): 1 207-1 211.
[27] Ushizawa K, Mikka N G, Watanabe K, et al. Raman spectroscopic study on {100} facet of boron-doped chemical-vapour-deposited diamond crystals with Fano line fitting[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 1999, 30(10): 957-961.
[28] 俞丹燕, 彭秋瑾, 张旭, 等. 不同激发波长下典型化学气相沉积法合成钻石拉曼光谱异同特征[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(23): 275-280. Yu D Y, Peng Q J, Zhang X, et al. Similarities and differences of raman spectra of typical chemical vapor deposition-grown synthetic diamonds under different excitation wavelengths[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(23): 275-280. (in Chinese)
[29] Martineau P M, Lawson S C, Taylor A J, et al. Identification of synthetic diamond grown using chemical vapor deposition(CVD)[J]. Gems & Gemology, 2004, 40(1): 2-25.



 下载:
下载: