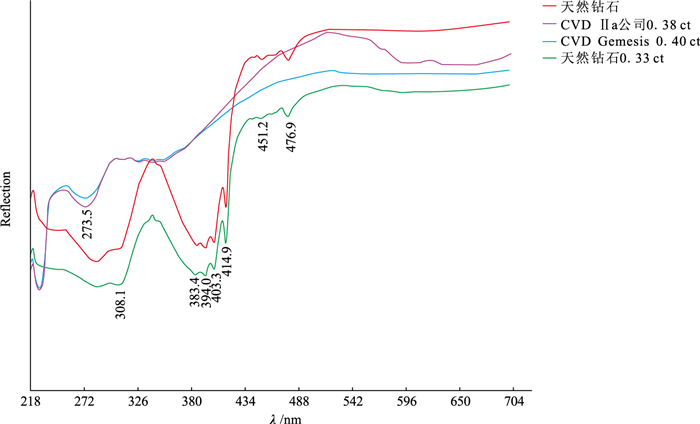
UV-Vis-NIR spectra of natural diamond, CVD Gemesis 0.4 ct and CVD Ⅱa company 0.38 ct lab-grown dianonds, and 0.33 ct natural diamond
Figures of the Article
-
![]() HPHT lab-grown diamonds adsorbed by strong magnet
HPHT lab-grown diamonds adsorbed by strong magnet
-
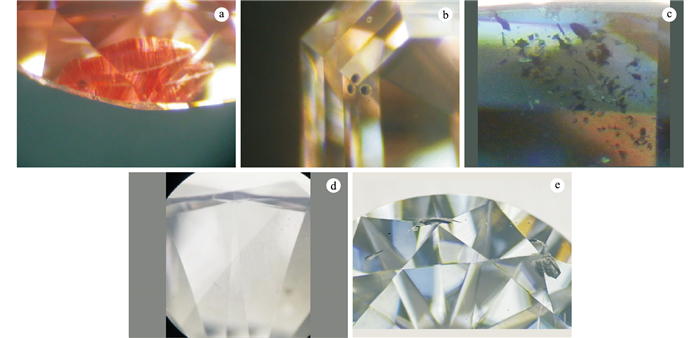
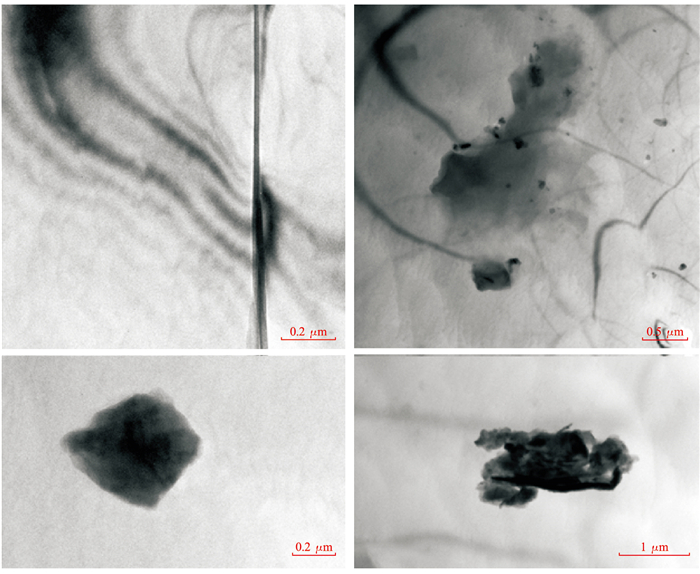
![]() The inclusions characteristics of lab-grown diamonds: a.Zigzag like feather crack in CVD lab-grown diamond; b.Cotton ball shape inclusions in CVD lab-grown diamond; c.Polycrystalline spots close to the surface in CVD lab-grown diamond; d.The entire layer of fine mesh impurities in CVD lab-grown diamond; e.HPHT lab-grown diamonds with black catalyst metal inclusions inside
The inclusions characteristics of lab-grown diamonds: a.Zigzag like feather crack in CVD lab-grown diamond; b.Cotton ball shape inclusions in CVD lab-grown diamond; c.Polycrystalline spots close to the surface in CVD lab-grown diamond; d.The entire layer of fine mesh impurities in CVD lab-grown diamond; e.HPHT lab-grown diamonds with black catalyst metal inclusions inside
-
![]() UV-Vis-NIR spectra of natural diamond, CVD Gemesis 0.4 ct and CVD Ⅱa company 0.38 ct lab-grown dianonds, and 0.33 ct natural diamond
UV-Vis-NIR spectra of natural diamond, CVD Gemesis 0.4 ct and CVD Ⅱa company 0.38 ct lab-grown dianonds, and 0.33 ct natural diamond
-
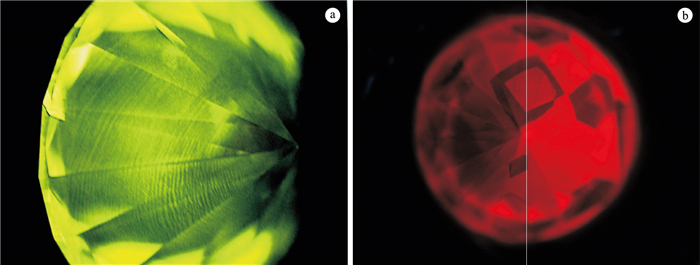
![]() Very few CVD diamomds show shell like pattern characteristic[1](a) and a HPHT lab-grown diamond with a larger square (100) face structure in the center of the diamond and four cross-symmetrical small square structure (three are visible in this picture) on the periphery of the diamond(b)
Very few CVD diamomds show shell like pattern characteristic[1](a) and a HPHT lab-grown diamond with a larger square (100) face structure in the center of the diamond and four cross-symmetrical small square structure (three are visible in this picture) on the periphery of the diamond(b)
-
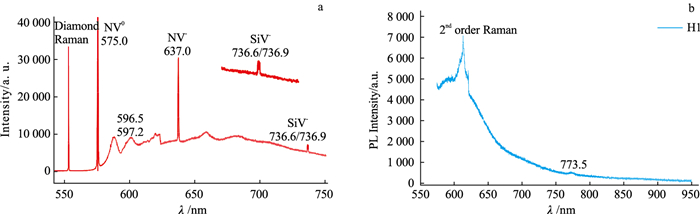
![]() Photoluminescence of CVD lab-grown diamonds at low temperature in liquid nitrogen showing the small peaks at 596.5, 597.2 nm and clear Si-V peaks at 736.6/736.9 nm(a)[2] and photoluminescence of a HPHT lab-grown diamond showing 773.5 nm peak revealing cobalt metal catalyst(b)
Photoluminescence of CVD lab-grown diamonds at low temperature in liquid nitrogen showing the small peaks at 596.5, 597.2 nm and clear Si-V peaks at 736.6/736.9 nm(a)[2] and photoluminescence of a HPHT lab-grown diamond showing 773.5 nm peak revealing cobalt metal catalyst(b)
-
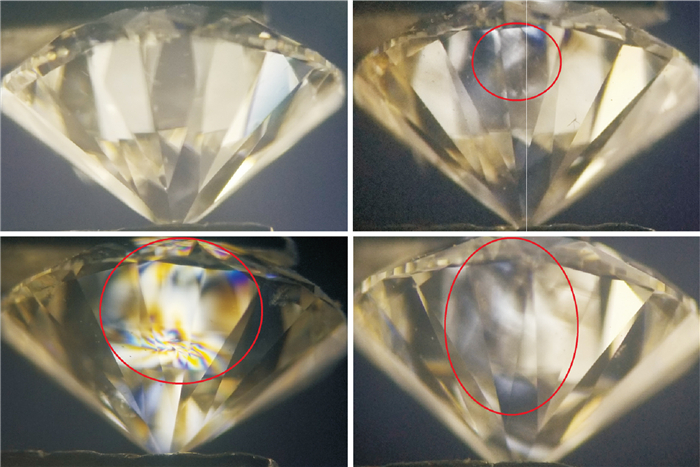
![]() Stress characteristics of natural diamonds under crossed polarizing filters: No stress in all areas or stress patterns in some areas
Stress characteristics of natural diamonds under crossed polarizing filters: No stress in all areas or stress patterns in some areas
-
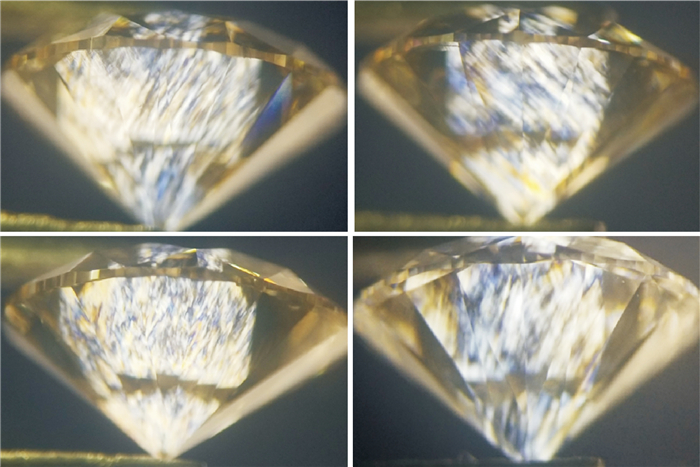
![]() CVD lab-grown diamonds without coulour treatment under crossed polarizing filters showing thick, sparse, skewed, oblique and nearly parallel stripes
CVD lab-grown diamonds without coulour treatment under crossed polarizing filters showing thick, sparse, skewed, oblique and nearly parallel stripes
-
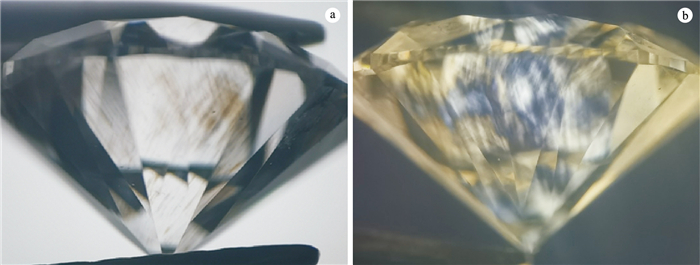
![]() The natural brown type Ⅱa diamond treated by HPHT into colourless diamond. Under crossed polarizing filters, there are full stripes, and some areas have thin, dense, flat and straight cross lines
The natural brown type Ⅱa diamond treated by HPHT into colourless diamond. Under crossed polarizing filters, there are full stripes, and some areas have thin, dense, flat and straight cross lines
-
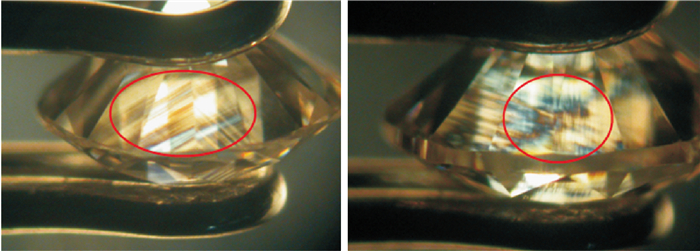
![]() Characteristics of CVD lab-grown diamonds after HPTH colour treatment under crossed polarizing filters: a.Gray-black column, with serious HPHT colour treatment; b.Gray-blue column, with slight HPHT colour treatment
Characteristics of CVD lab-grown diamonds after HPTH colour treatment under crossed polarizing filters: a.Gray-black column, with serious HPHT colour treatment; b.Gray-blue column, with slight HPHT colour treatment
-
![]() Lightbox CVD lab-grown diamond without colour treatment showing no column
Lightbox CVD lab-grown diamond without colour treatment showing no column
-
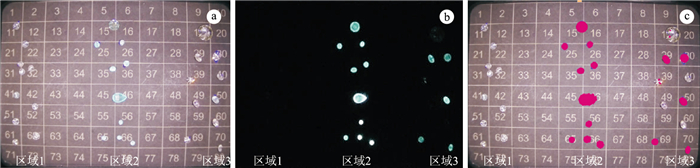
![]() phosphorescent characteristics of natural diamonds(area 1), HPHT(area 2) and CVD (area 3) lab-grown diamonds: a.The luminous state of the diamonds when irradiated by ultra-shortwave ultraviolet light; b.After the ultra-shortwave ultraviolet light is turned off, the phosphorescent luminescence state of the diamonds, area 1 shows no phosphorescence, area 2 shows phosphorescence, and area 3 shows medium, weak or none phosphorescence; c.The instrument automatically converts phosphorescence of different intensities into red. Diamonds with strong phosphorescence show all red, diamonds with medium phosphorescence are mostly red, diamonds with weak phosphorescence show red in some area, if there is no phosphorescence, no red shows
phosphorescent characteristics of natural diamonds(area 1), HPHT(area 2) and CVD (area 3) lab-grown diamonds: a.The luminous state of the diamonds when irradiated by ultra-shortwave ultraviolet light; b.After the ultra-shortwave ultraviolet light is turned off, the phosphorescent luminescence state of the diamonds, area 1 shows no phosphorescence, area 2 shows phosphorescence, and area 3 shows medium, weak or none phosphorescence; c.The instrument automatically converts phosphorescence of different intensities into red. Diamonds with strong phosphorescence show all red, diamonds with medium phosphorescence are mostly red, diamonds with weak phosphorescence show red in some area, if there is no phosphorescence, no red shows
-
![]() HPHT lab-grown diamonds detected on the inlaid jewelry
HPHT lab-grown diamonds detected on the inlaid jewelry
-
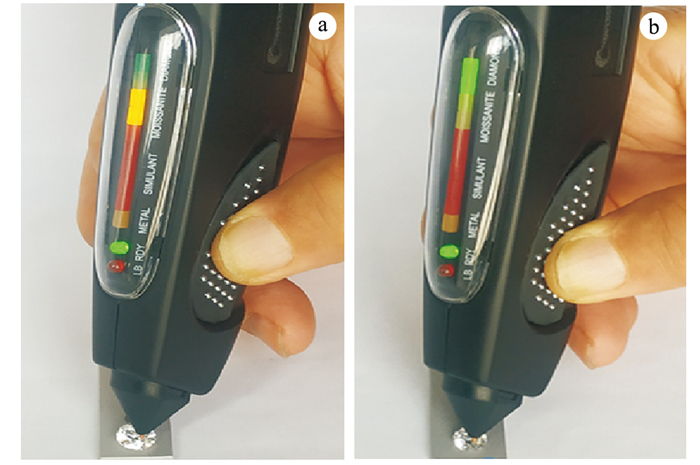
![]() Results of thermal conductometer of lab-grown diamonds: a.Some HPHT lab-grown diamonds show MOISSANITE, and some show DIAMOND; b.CVD lab-grown diamonds show DIAMOND
Results of thermal conductometer of lab-grown diamonds: a.Some HPHT lab-grown diamonds show MOISSANITE, and some show DIAMOND; b.CVD lab-grown diamonds show DIAMOND
-
![]() Inclined lines and dislocation couples of HPHT synthetic diamond with dark red colour changed by irradiation
Inclined lines and dislocation couples of HPHT synthetic diamond with dark red colour changed by irradiation
-
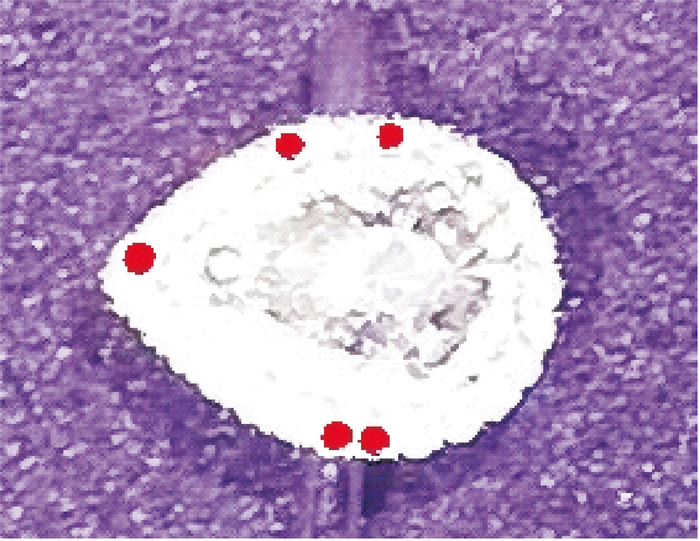
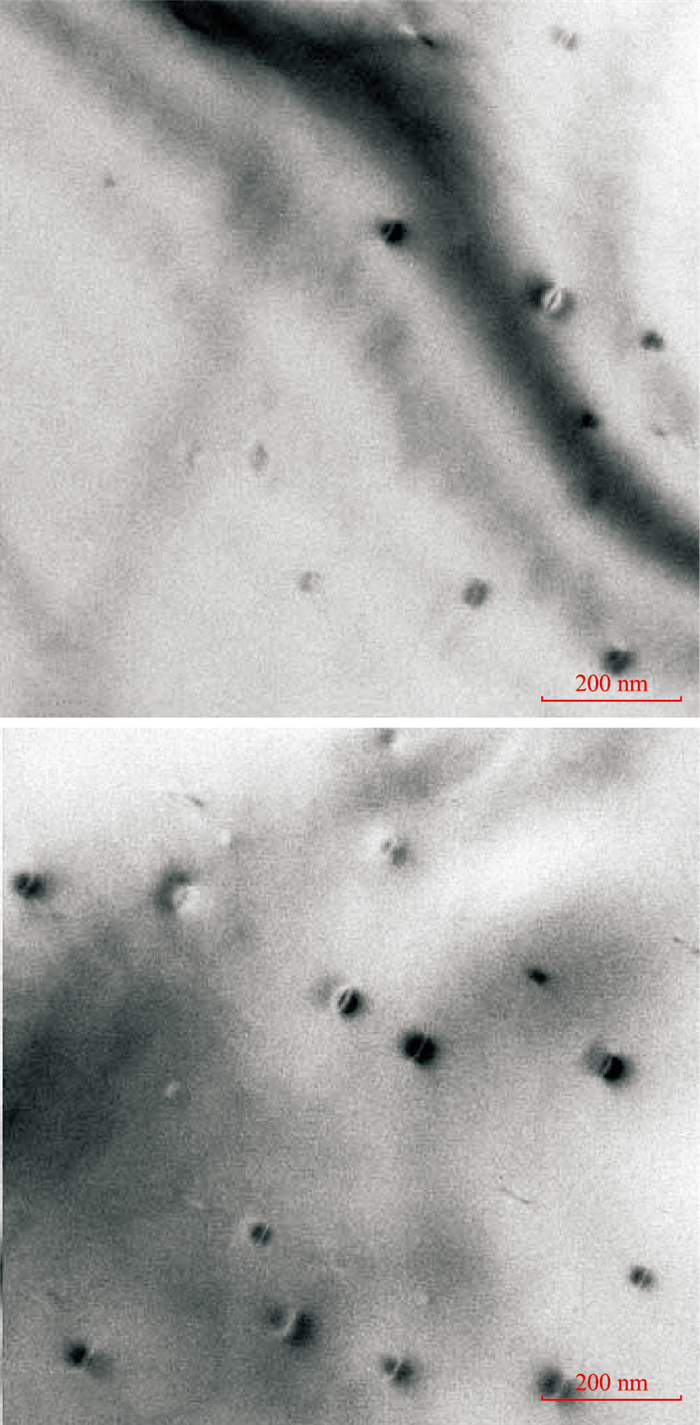
![]() Tinny black graphite inclusion, equal inclination fringe lines and dislocations in CVD lab-grown diamond by TEM
Tinny black graphite inclusion, equal inclination fringe lines and dislocations in CVD lab-grown diamond by TEM
-
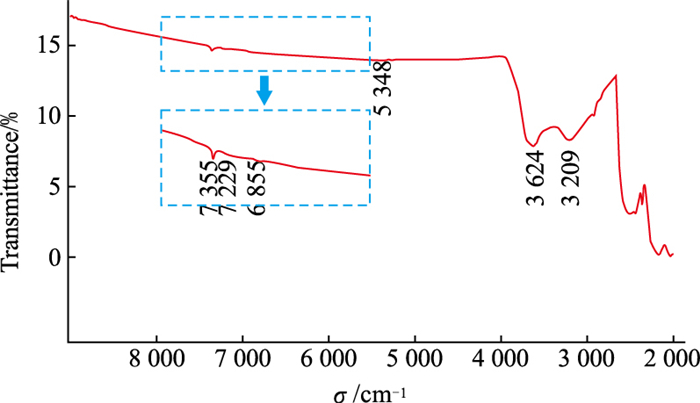
![]() FTIR of CVD lab-grown diamonds without HPHT treatment
FTIR of CVD lab-grown diamonds without HPHT treatment


 Download:
Download: