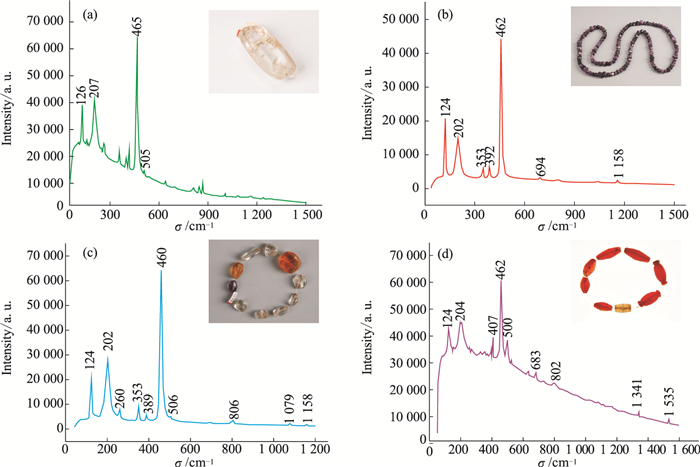
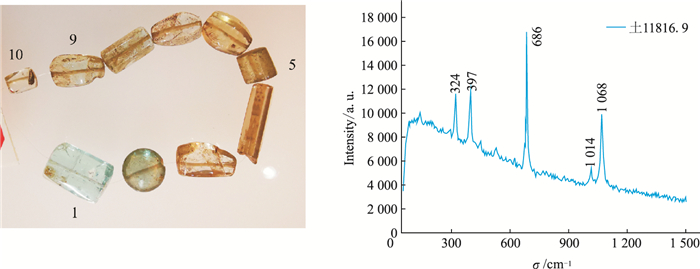
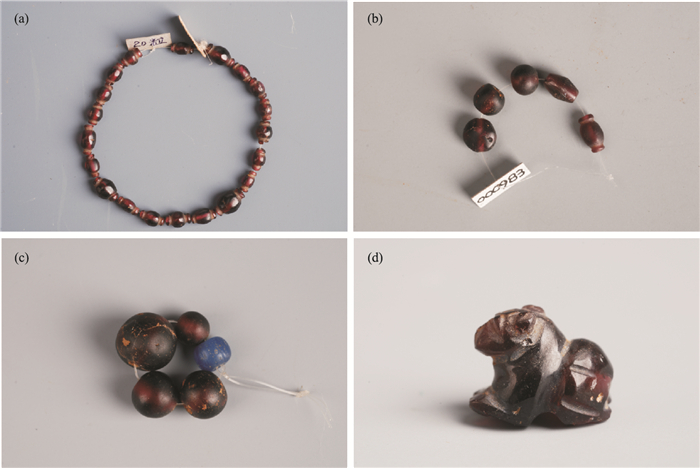
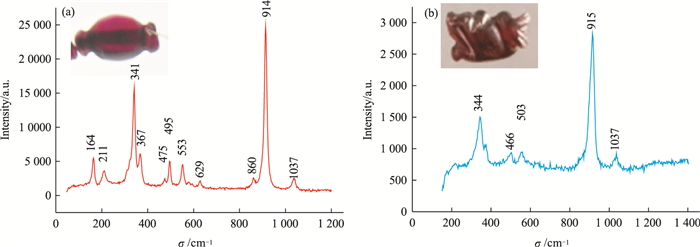
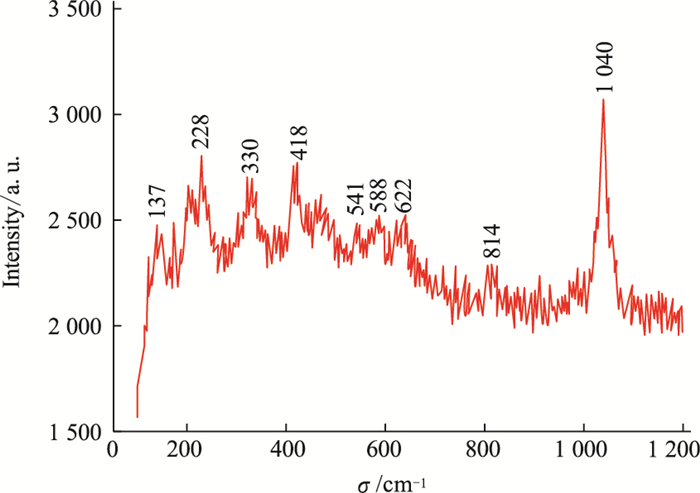
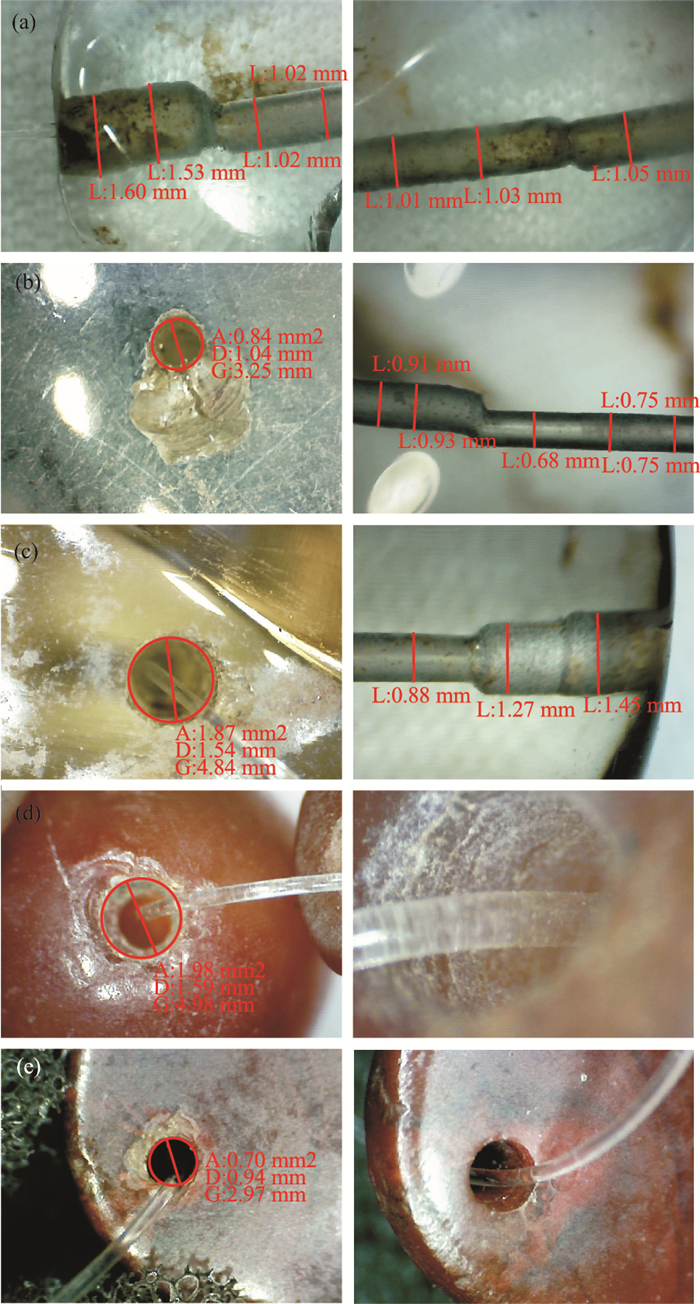
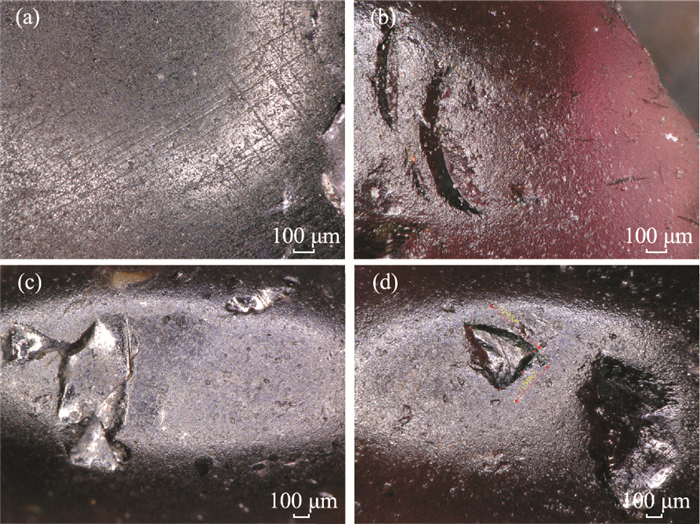
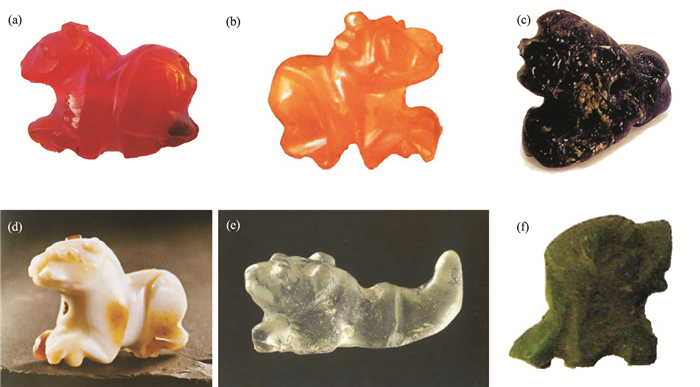
| [1] |
Bednarik R G. The significance of the earliest beads[J]. Advances in Anthropology, 2015, 5(2): 51-66. doi: 10.4236/aa.2015.52006
|
| [2] |
Brandherm D, Heymans E, Hofmann D. Gift, goods and money[M]. Oxford: Archaeopress Publishing Ltd., 2018.
|
| [3] |
Beck H C. Classification and nomenclature of beads and pendants[J]. Beads: Journal of the Society of Bead Researchers, 2006(18): 1-76.
|
| [4] |
Dubin L S. The history of beads: From 100, 000 BC to the present[M]. NewYork: Abrams, 2009.
|
| [5] |
夏鼐. 古代埃及珠子的考古价值. 夏鼐文集(下)[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2000.
Xia N. Archaeological value of the ancient Egyptian beads. Collected works of Xia Nai[M]. Beijing: Social Sciences Academic Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
|
| [6] |
李青会, 左骏, 刘琦, 等. 文化交流视野下的汉代合浦港[M]. 南宁: 广西科技出版社. 2019.
Li Q H, Zuo J, Liu Q, et al. Research on the Hepu port of the Han Dynasty from the perspective of cultural exchange[M]. Nanning: Guangxi Science & Technology Publishing House, 2019. (in Chinese)
|
| [7] |
熊昭明. 汉代合浦港考古与海上丝绸之路[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2015.
Xiong Z M. Archaeological discovery: The Hepu port on the Maritime Silk Road of the Han Dynasty[M]. Beijing: Cultural Relics Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
|
| [8] |
熊昭明. 汉代合浦港的考古学研究[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2018.
Xiong Z M. Archaeological study of the Hepu port in the Han Dynasty[M]. Beijing: Cultural Relics Press, 2018. (in Chinese)
|
| [9] |
富霞. 合浦汉墓研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2023.
Fu X. Study on Han tombs in Hepu[M]. Beijing: China Science Publishing & Media Ltd., 2023. (in Chinese)
|
| [10] |
Liu S, Li Q H, Gan F, et al. Silk Road glass in Xinjiang, China: Chemical composition analysis and interpretation using a high-resolution portable XRF spectrometer[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2012(39): 2 128-2 142.
|
| [11] |
刘松, 郭木森, 董俊卿, 等. 宝丰清凉寺窑(汝窑)遗址出土陶瓷器的科学研究[M]//河南省文物考古研究院, 宝丰汝窑博物馆. 宝丰清凉寺窑. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 329-501.
Liu S, Guo M S, Dong J Q, et al. Scientific research on ceramics unearthed at the site of Baofeng Qingliang Temple Kiln (Ru Kiln) Site[M]//Henan Provincial Institute of Cultural Heritage and Archaeology, Ru Kiln Museum of Baofeng. Baofeng Qingliang Temple Kiln. Beijing: China Science Publishing & Media Ltd., 2020: 329-501. (in Chinese)
|
| [12] |
董俊卿, 李青会, 刘松. 合浦汉墓出土绿柱石宝石珠饰的科学分析[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 2019, 31(4): 30-38.
Dong J Q, Li Q H, Liu S. Scientific analysis of beryl bead ornaments unearthed from Han tombs in Hepu county[J]. Sciences of Conservation and Archaeology, 2019, 31(4): 30-38. (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
Price M, Walsh K. Pocket nature rocks and minerals[M]. Singapore: South China Printing Co., Ltd., China, 2005.
|
| [14] |
Charoy B, De Donato P, Baries O, et al. Channel occupancy in an alkaline-poor beryl from Serra Branca (Goias, Brazil): Spectroscopic characterization[J]. American Mineralogist, 1996, 81(3-4): 395-403. doi: 10.2138/am-1996-3-414
|
| [15] |
Theo Kloprogge J, Frost R L. Raman microscopic study at 300 and 77 K of some pegmatite minerals from the Iveland-Evje area, Aust-Agder, Southern Norway[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2000, 56 (3): 501-513. doi: 10.1016/S1386-1425(99)00141-9
|
| [16] |
Barton M D, Young S. Non-pegmatitic deposits of beryllium: Mineralogy, geology, phase equilibria and origin[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry. 2002, 50(1): 591-691. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2002.50.14
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
李亚光. 不同产地的绿松石特征浅析[J]. 文物鉴定与鉴赏, 2017(6): 82-83.
Li Y G. Primary study on characteristics of turquoise from different origins[J]. Identification and Appreciation of Cultural Relics, 2017(6): 82-83. (in Chinese)
|
| [19] |
周佩玲. 系统宝石学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2004: 147.
Zhou P L. Systematic gemology[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2004: 147. (in Chinese)
|
| [20] |
张蓓莉. 系统宝石学[M]. 2版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006: 542-549.
Zhang P L. Systematic gemmology[M]. 2 Edition. Beijing: Geology Press, 2006: 542-549. (in Chinese)
|
| [21] |
Liu Q, Liu S, Lyu L B, et al. Scientific analysis of ancient amber artifacts along the Maritime Silk Road[J]. Palaeoentomology, 2023, 6 (5): 451-454.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
Saminpanya S, Saiyasombat C, Chanlek N, et al. Trace elements content and cause of color in ancient treated carnelian and its natural counterpart from SE Asia[J]. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2020, 12(1): 3. doi: 10.1007/s12520-019-00953-x
|
| [24] |
霍巍. 长江上游早期文明的探索[M]. 成都: 巴蜀书社, 2002: 146-175.
Huo W. The exploration of the early civilization in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Bashu Publishing House Co., Ltd., 2002: 146-175. (in Chinese)
|
| [25] |
李钰. 中国古代蚀花石珠源流探析[J]. 文物天地, 2018(1): 27-36.
Li Y. Study on etched beads found in ancient China[J]. Cultural Relics World, 2018(1): 27-36. (in Chinese)
|
| [26] |
广州市文物考古研究院. 广州出土汉代珠饰研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020.
Guangzhou Municipal Institute of Cultural Heritage and Archaeology. Study on the beads and pendants of Han Dynasty unearthed from Guangzhou[M]. Beijing: China Science Publishing & Media Ltd., 2020. (in Chinese)
|
| [27] |
Groman-Yaroslavski I, Mayer D B. Lapidary technology revealed by functional analysis of carnelian beads from the early Neolithic site of Nahal Hemar Cave, southern Levant[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015(58): 77-88.
|
| [28] |
Bellina B. Maritime Silk Roads'ornament industries: Socio-political practices and cultural transfers in the South China Sea[J]. Cambridge Archaeological Journal, 2014, 24(3): 345-377. doi: 10.1017/S0959774314000547
|
| [29] |
Bellina B. Beads, social change and interaction between India and South-east Asia[J]. Antiquity, 2015, 77(296): 285-297.
|
| [30] |
Rajan K, Athiyaman N. Traditional gemstone cutting technology of Kongu region in Tamil Nadu[J]. Indian Journal of History of Science, 2004, 39(4): 385-414.
|
| [31] |
Biswas K A. Vaidūrya, marakata and other beryl family gem minerals: Etymology and traditions in ancient India[J]. Indian Journal of History of Science, 1994, 29(2): 139-154.
|
| [32] |
Schmetzer K, Albert G H, Schüssler U J, et al. The linkage between garnets found in India at the Arikamedu archaeological site and their source at the Garibpet deposit[J]. The Journal of Gemmology, 2017, 35(7): 598-627. doi: 10.15506/JoG.2017.35.7.598
|
| [33] |
Francis J P. The stone bead industry of Southern India[J]. Beads: Journal of the Society of Bead Researchers, 2000(12): 49-62.
|
| [34] |
Francis J P. Final report on Arikamedu, India[J]. The Margaretologist, 2001, 13(2): 1-12.
|
| [35] |
Carter A K. Garnet beads in Southeast Asia: Evidence for local production?[C]//Tjoa-Bonatz M, Reinecke A, Bonatz D. Crossing Borders: Selected Papers from the 13th International Conference of the European Association of Southeast Asian Archaeologists. Singapore: NUS Press, 2012: 296-306.
|
| [36] |
Yamagata M, Manh P D, Hoang B C. Western Han bronze mirrors recently discovered in Central and Southern Viet Nam[J]. Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association, 2008(21): 99-106.
|
| [37] |
Buddikasiri P R A, Madhumali A K R. Glass bead making technology in ancient Sri Lanka[J]. Journal of Archaeology, 2020, 1(2): 144-165.
|
| [38] |
Reinecke A, Laychour V, Sonetra S. The first golden age of Cambodia: Excavation at Prohear[M]. Bad Langensalza: Thomas Müntzer, 2009.
|
| [39] |
Bellina B, Glover I C. The archaeology of early contacts with India and the Mediterranean world from the fourth century BC to the fourth Century AD[M]//Glover I C, Bellwood P. Southeast Asia from the Prehistory to History. London: Routledge Curzon Press, 2004: 68-88.
|
| [40] |
Bellina B. The inception of the trans-national processes between the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea from an early city-state on the Thai-Malay Peninsula (4th to 2nd c. BCE)[M]//Boussac M F, Roychoudhury S, Salles J F, et al. The Ports of the Indian Ocean, from the Red Sea to the Gulf of Bengal. Delhi: Primus Books, 2016: 463-489.
|
| [41] |
孔德安. 浅谈我国新石器时代绿松石器及制作工艺[J]. 考古, 2002(5): 74-80.
Kong D A. Primary study on turquoise ware and production technology in the Neolithic age in China[J]. Archaelogy, 2002(5): 74-80. (in Chinese)
|
| [42] |
霍巍, 赵德云. 战国秦汉时期中国西南的对外文化交流[M]. 成都: 巴蜀书社, 2007: 103.
Huo W, Zhao D Y. Cultural exchanges between Southwest China and foreign countries during the Warring States Period to Qin and Han dynasties[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Bashu Publishing House Co., Ltd., 2007: 103. (in Chinese)
|
| [43] |
刘琦, 张艳华, 李星枰, 等. 几件湖南汉墓出土的琥珀制品研究[J]. 宝石和宝石学杂志(中英文), 2023, 25(4): 1-12.
Liu Q, Zhang Y H, Li X P, et al. Some amber artifacts excavated from tombs of the Han Dynasty in Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2023, 25(4): 1-12. (in Chinese)
|
| [44] |
云南省文物考古研究所, 玉溪市文物管理所, 江川县文化局. 江川李家山——第二次发掘报告[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2007: 221.
Yunnan Provincial Institute of Cultural Heritage and Archaeology, Yuxi Municipal Institute of Cultural Heritage, Culture Bureau of Jiangchuan county. Lijiashan in Jiangchuan: Reports for the second excavation[M]. Beijing: Cultural Relics Press, 2007: 221. (in Chinese)
|
| [45] |
张增祺. 晋宁石寨山[M]. 昆明: 云南美术出版社, 1998: 104-214.
Zhang Z Q. Shizhaishan in Jinnin[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Art Press, 1998: 104-214. (in Chinese)
|
| [46] |
云南省文物考古研究所, 红河哈尼族彝族自治州文物管理所, 个旧市博物馆. 个旧市黑蚂蚁井墓地第四次发掘报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 图版三七.
Yunnan Provincial Institute of Cultural Heritage and Archaeology, Institute of Cultural Heritage of Honghe Hani and Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Museum of Gejiu. Reports of forth excavation for the tombs of Black Ant well in Gejiu city[M]. Beijing: China Science Publishing & Media Ltd., 2013: Plate 37. (in Chinese)
|
| [47] |
喻燕姣. 湖南出土珠饰研究[M]. 长沙: 湖南人民出版社, 2018.
Yu Y J. Study on beads and ornaments found in Hunan[M]. Changsha: Hunan People's Publishing House, 2018. (in Chinese)
|
| [48] |
刘云辉. 陕西出土汉代玉器[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2009.
Liu Y H. Jade articles of Han Dynasty excavated from Shaanxi Province[M]. Beijing: Cultural Relics Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
Beck H C. The beads from Taxila (Memoirs of the archaelolgocal survey of India No. 65)[M]. New Delhi: The Director General Archaeological Survey of India Janpath, 1999.
|
| [51] |
班查·彭帕宁. 一定要收藏的古珠天珠珍贵图鉴[M]. 林璟玟, 译. 台湾新北市: 维他命文化有限公司, 2013.
Pongpanich B. Beyond beads[M]. Lin J W, Translated. Xinbei (Taiwan, China): Vitamin Books Co., Ltd., 2013. (in Chinese)
|
| [52] |
Chaisuwan B. Early contacts between India and the Andaman Coast in Thailand from the second century BCE to eleventh century CE[M]//Manguin P Y, Mani A, Wade G. Early Interactions between South and Southeast Asia: Reflections on Cross-Cultural Exchange. Singapore: ISEAS Publishing, 2011: 83-112.
|
| [53] |
Dzung L T M. Central Vietnam during the Period from 500 BCE to CE500[M]//Manguin P Y, Mani A, Wade G. Early Interactions between South and Southeast Asia: Reflections on Cross-Cultural Exchange. Singapore: ISEAS Publishing, 2011: 3-15.
|
| [54] |
Tan T. Ancient jewellery of Myanmar: From Prehistory to Pyu Period[M]. Yangon: Mudon Sar Pae Publishing House, 2015.
|



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: